Use Workflows
A workflow is a sequence of tasks that are triggered by an action, a condition or a rule. Workflows are usually implemented to integrate business logic to an organization, such as the separation of duties, unifying processes, or to increase trust and responsibilities.
The workflows are designed to create requests for approval of a new value while keeping the old value in case the request is not approved. The new value will not be implemented until the last request is approved.
The business logic could be approval of:
- New master data like G/L Accounts, customers, vendors, or items
- Changes to fields in existing records containing sensible information, such as Vendor Bank Account No. or Customer Credit Limit
- Changes to fields in existing records containing business critical information, such as Item Sales Prices
- New users or changes to user permissions
- Purchase documents
- Sales documents
- Incoming documents
- Finance journals prior to posting
The following illustration shows an example of a workflow with sequential approval triggered by a user. By triggering the workflow, an approval request is created for the first approver.
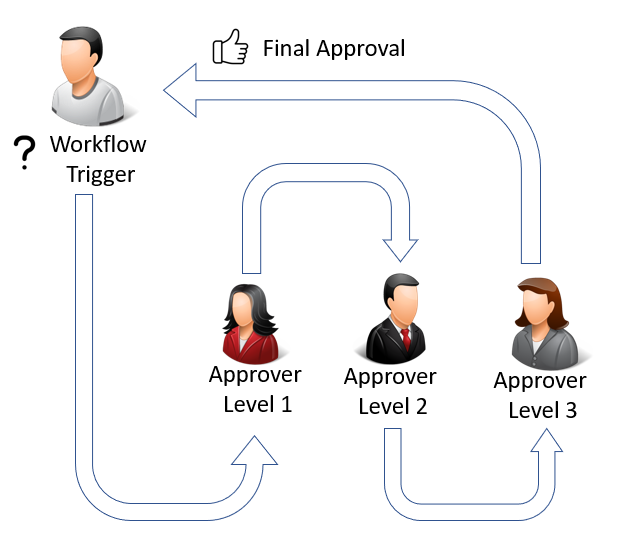
In this example, the request must be approved by the first approver before the request is sent on to the next approver. If the request is not approved by the first approver, the request will never go to the next approver.
The route taken from the initial triggering of the workflow can vary depending on the nature of the approval.
The following illustration shows a parallel approval that is triggered by the user. By triggering the workflow, an approval request is sent to all approvers simultaneously.
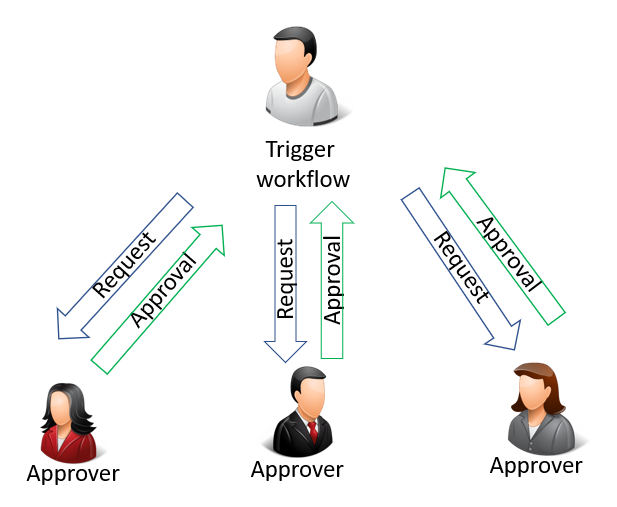
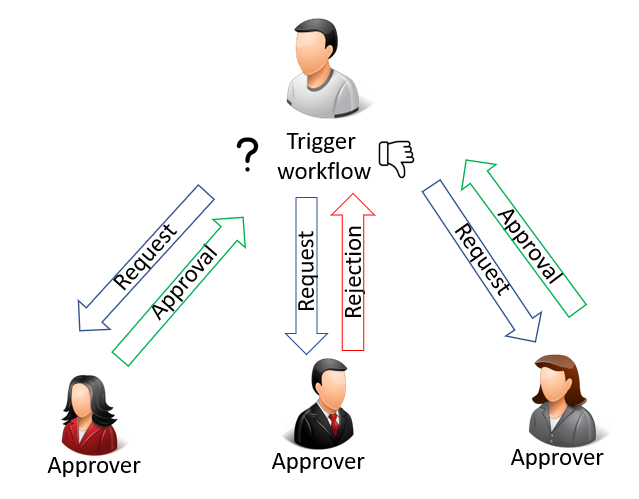
However, the workflow is not approved until all requests have been approved by the approvers, as shown in the following illustration:
[!NOTE]
It is not possible to create a workflow with multiple approvers and expect the whole workflow to be approved after the first request has been approved. All requests must be approved for the workflow to be approved.
You can set up and use workflows that connect business-process tasks performed by different users. It is also possible to create the same workflow more than once. Each workflow triggered by en event using different filters. This is useful if an approval request in one department must be approved by one approver, where approval requests in other departments must be approved by another approver. System tasks, such as automatic posting, can be included as steps in workflows, preceded or followed by user tasks. Requesting and granting approval to create new records are typical workflow steps.
Before you can begin to use workflows, you must set up workflow users, create the workflows, potentially preceded by code customization and specify how users receive notifications. For more information, see Setting Up Workflows.
[!NOTE]
Typical workflow steps are about users who request approval of tasks and approvers accepting or rejecting approval requests. Therefore, many topics about how to use workflows refer to approvals.
The following table describes a sequence of tasks, with links to the topics that describe them.
| To | See |
|---|---|
| Set a workflow to start when the first entry-point event occurs. | Enable Workflows |
| Request approval of a task, as an approver, accept, decline, or delegate approvals, and send or view approval notifications. | Use Approval Workflows |
| Create workflow steps that restrict a certain record type from being used before a certain event occurs, for example that the record is approved. | Restrict and Allow Usage of a Record |
| View workflow step instances of status Completed. | View Archived Workflow Step Instances |
| Delete a workflow that you are sure will no longer be used. | Delete Workflows |
See Also
Setting Up Workflows
Workflow
Work with Business Central
--- author: edupont04
